

- #NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP HOW TO#
- #NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP INSTALL#
- #NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP MAC#
- #NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP WINDOWS#
#NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP WINDOWS#
Windows devices maintain an ARP cache, which contains the results of recent ARP queries.
#NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP MAC#
Its job is to map IP addresses to MAC addresses. This is where the Address Resolution Protocol comes into play. Although it is easy to think of network communications in terms of IP addressing, packet delivery is ultimately dependent on the Media Access Control (MAC) address of the device’s network adapter. The ARP command corresponds to the Address Resolution Protocol. To see this type of summary information, just type NetStat -e. This command has a number of different functions, but the most useful of these is to display network summary information for the device.
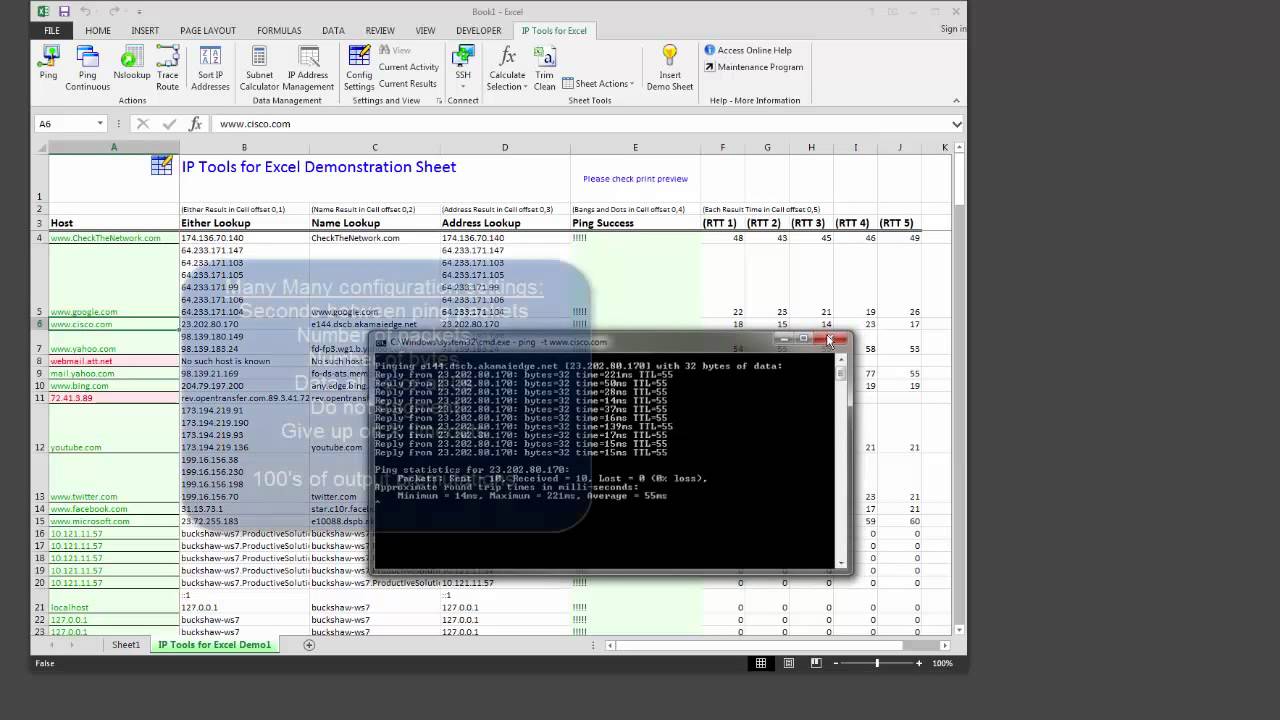
That’s where the aptly named NetStat command comes into play. If you are experiencing problems with network communications, then network statistics can sometimes help point you toward the root cause of the problem. Receiving these packets confirms that a valid and functional network path exists between the two hosts. Assuming that there are no network problems or firewalls preventing the ping from completing, the remote host will respond to the ping with four packets. Simply enter the Ping command, followed by the name or the IP address of the destination host. Ping is used to test the ability of one network host to communicate with another. I am guessing that the ping command is probably the most familiar, and most widely used of the utilities being discussed in this article, but that does not make it any less essential. However, there are 11 built-in networking tools that Windows networking administrators should be familiar with. These tools range from the obscure to the commonplace.
#NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP INSTALL#
We do hope that you can now comfortably install the utilities when confronted with a system without them.The Windows operating system contains numerous built-in, command line networking utilities.
#NETWORK TOOLS NSLOOKUP HOW TO#
In this article, you learned how to install dig and nslookup command utilities in different Linux distributions and also the basic usage of the commands. To retrieve information about a domain name using the nslookup utility, use the following command. To check the MX record of the domain name run. To get more specific and display only the IP of the domain name append the +short argument as shown: # dig +short flags: qr rd ra QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 2, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 1 >HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 58049

Sample Output > DiG 9.11.3-1ubuntu1.9-Ubuntu > The command displays a host of information such as the version of the dig command utility, the DNS server, and its corresponding IP address. # dig -vĬheck dig Version in Arch Linux Using the dig commandĭig command can be used to query a domain name and retrieve information as shown: # dig To check the version of dig installed, run. # dig -vĬheck dig Version in Debian and Ubuntu Installing dig & nslookup on ArchLinuxįor ArchLinux, the command for installing dig and nslookup will be. # apt install dnsutilsĪgain, to verify the installation, run the command. On Debian and any of its derivatives including Debian, the installation is done using the apt command. # dig -vĬheck Dig Command Version Installing dig & nslookup on Debian / Ubuntu Upon successful installation, verify the version using the command below. On Red Hat Linux /CentOS, install dig and nslookup using the dnf command.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
